MVR Evaporator | 80% Energy Saving Mechanical Vapor Recompression System for Wastewater & Pharma
Product Overview Revolutionize your concentration process with our MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) Evaporator. Unlike traditional multi-effect evaporation systems, our MVR technology recovers and compresses 100% of the secondary steam, converting waste heat into reusable energy.
The result? A system that saves over 80% of energy and requires zero live steam during normal operation.
Company Name :
Yan Jialong Mechanical Technology(Jiangsu)Co.,Ltd.Brand :
Yanjialong TechnologyYanjialong Mechanical Technology (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. is a service provider focusing on evaporation (concentration) crystallization equipment. Adhering to the beautiful vision of "recycling every drop of water", we have always focused on the research and development, design and manufacturing of evaporator technology products, and have an experienced technical team.
Yanjialong is currently a high-tech evaporator enterprise with a full range of pilot equipment for multi-effect evaporators, falling film evaporator pilot equipment, and MVR evaporator pilot equipment in China. At present, the company has a relatively large evaporator R&D and production base, with its own production workshop and laboratory test equipment, which can conduct material analysis for customers in a timely manner.
Yanjialong Company has more than 10 years of engineering experience and performance in testing, design, processing, installation, commissioning and after-sales service, with a technical team of more than 30 people. The company has obtained a number of high-tech enterprise certificates through the ISO9001 quality certification system, and has a number of patents for various inventions and utility models, many of which have reached the domestic forefront level, the company is committed to making the water clearer, the sky bluer, and the environment more beautiful.
MVR Evaporator,
Multi-effect Evaporator,
Bring Drying Machine, Single-effect Evaporator,
Film Scraper Evaporator
Descriptions
MVR evaporator (mechanical vapor recompression) is a term for the technology that reuses the energy from its own generated secondary steam, thereby reducing the demand for external energy.
The secondary steam, after being compressed by the compressor, has its pressure and temperature increased, resulting in an increase in thermal enthalpy, which is then sent to the heating chamber of the evaporator to be used as heating steam (i.e., live steam) to maintain the material solution in an evaporating state, while the heating steam itself transfers heat to the material and condenses into water. In this way, the steam that was originally to be discarded is fully utilized, recovering latent heat and improving thermal efficiency.
As early as the 1960s, Germany and France successfully applied this technology in industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, paper making, wastewater treatment, and seawater desalination.
The working process involves low-temperature steam being compressed by the compressor, raising its temperature and pressure, and increasing its thermal enthalpy, before entering the heat exchanger to condense, thus fully utilizing the latent heat of the steam.
Apart from startup, the entire evaporation process does not require live steam. In a multi-effect evaporation process, the secondary steam from a particular effect cannot be used directly as the heating source for that effect; it can only serve as a heating source for the subsequent effect or the next one. If it is to be used as the heating source for that effect, additional energy must be supplied to raise its temperature (pressure). Steam jet pumps can only compress some of the secondary steam, while MVR evaporators can compress all of the secondary steam in the evaporator.
The solution circulates through a falling film evaporator via a material circulation pump inside the heating tubes. The initial steam is heated by fresh steam outside the tubes, causing the solution to boil and generate secondary steam, which is sucked in by a turbo blower. After compression, the temperature of the secondary steam increases and enters the heating chamber as a heat source for cyclic evaporation. After normal startup, the turbo compressor sucks in the secondary steam, compresses it, and transforms it into heating steam, thus continuously performing cyclic evaporation. The evaporated moisture ultimately becomes condensate and is discharged.
Application
This equipment is suitable for industries such as pharmaceuticals, biology, food, and chemical engineering, and is commonly used for the evaporation and concentration of traditional Chinese medicine extracts, fruit juices, fine chemical solutions, and wastewater.
Features
(1) Low energy consumption and low operating costs. Theoretically, using an MVR evaporator can save more than 80% of energy compared to traditional evaporation equipment; in practice, the energy required to evaporate 1000 kg of moisture is only 1/6 to 1/5 of that of traditional evaporators (note: energy consumption varies with different materials), and its operating costs are also significantly reduced, generally only 35-50% of those of traditional evaporators.
(2) Compact equipment with a small footprint. Compared to multi-effect evaporation, it can reduce the footprint by more than 50%.
(3) Fewer auxiliary engineering requirements. The heating chamber of the MVR serves as the steam condenser, eliminating the need for a separate steam condenser and a large circulating cooling water system, saving more than 90% of cooling water.
(4) Mainly uses electrical energy. Apart from requiring a small amount of industrial steam for heating during equipment startup, it only needs clean electrical energy during normal operation, without the need for industrial steam.
(5) Smooth operation with a high degree of automation. The MVR system controls the temperature, pressure, and speed of the system through DCS/PLC, industrial computers, and configuration software to maintain the evaporation balance in the system.
(6) Uses single-stage vacuum evaporation, with a low evaporation temperature (45-85°C), making it particularly suitable for the concentration of heat-sensitive materials.
Principle of work
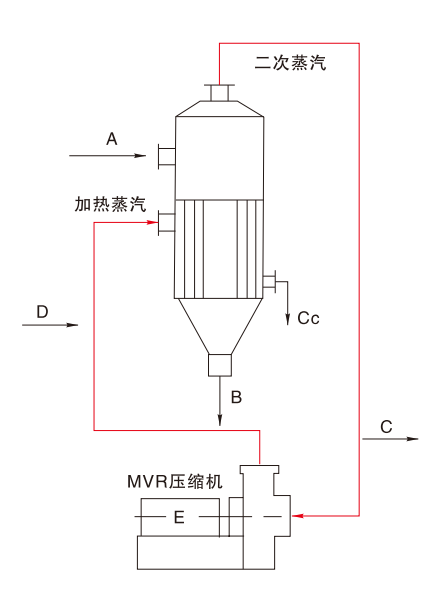
A Material B Concentrate C Residual steam Cc Steam condensate D Live steam replenishment (heat loss) E Thermal energy
(1) The electrical energy compresses the secondary vapor generated by evaporation and makes full use of it, with almost no loss of steam in the system.
(2) The heat energy from the condensate and concentrated liquid is exchanged with the original liquid.
(3) Non-condensable gas exchanges heat with the original liquid.
(4) The compressor motor uses variable frequency control.
MR technology can compress the secondary steam that needs to be condensed through a compressor to a higher pressure, thus increasing internal energy, achieving continuous circulation of this energy for reuse, and replacing fresh steam. By using a very small amount of electrical energy, a large amount of low-pressure steam internal energy can be reused, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for supply of fresh steam, recovering waste heat steam, reducing cooling water, and improving system utilization efficiency.
Comparison of multi-effect evaporation and MVR energy consumption (compared to three-effect at 10 tons per hour)
| Steam | Electricity | Total cost | |||
| Usage (degree) | Cost (Yuan) | Usage (degree) | Cost (Yuan) | ||
| Three effects | 5 | 1000 | 100 | 70 | 1070 |
| MVR | 0.2 | 40 | 500 | 350 | 390 |
| Water saved per ton | 680 | ||||
Based on steam at 200 yuan/ton, electricity cost at 0.7 yuan/kWh, calculated for 300 days a year, with 20 hours a day.